Thornley (1976 ) 提出了非直角双曲线模型,它的表达式为:
P_{n} = \frac{\alpha I + P_{nmax} \sqrt{(\alpha I + P_{nmax})^{2} - 4 \theta \alpha I P_{nmax}}}{2 \theta} - R_{d}
\tag{9.1}
其中,\theta 为表示曲线弯曲程度的曲角参数,取值为0\leq \theta \leq 1 。其他参数意义同式 公式 8.1 。同样如同直角双曲线模型,式仍然没有极值,无法求得 I_{sat} ,可以仍然参考直角双曲线模型的方式进行计算。
非直角双曲线模型的实现
Code library ( minpack.lm ) # 读取数据,同fitaci数据格式 lrc <- read.csv ( "data/lrc.csv" ) lrc <- subset ( lrc , Obs > 0 ) # 光响应曲线没有太多参数, # 直接调出相应的光强和光合速率 # 方便后面调用 lrc_Q <- lrc $ PARi lrc_A <- lrc $ Photo # 非直角双曲线模型的拟合 lrcnls <- nlsLM ( lrc_A ~ ( 1 / ( 2 * theta ) ) *
( alpha * lrc_Q + Am - sqrt ( ( alpha * lrc_Q + Am ) ^ 2 -
4 * alpha * theta * Am * lrc_Q ) ) - Rd ,
start= list ( Am= ( max ( lrc_A ) - min ( lrc_A ) ) ,
alpha= 0.05 ,Rd= - min ( lrc_A ) ,theta= 1 ) )
fitlrc_nrec <- summary ( lrcnls ) # 光补偿点 Ic <- function ( Ic ) { ( 1 / ( 2 * fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 4 ,1 ] ) ) *
( fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 2 ,1 ] * Ic + fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 1 ,1 ] -
sqrt ( ( fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 2 ,1 ] * Ic + fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 1 ,1 ]
) ^ 2 - 4 * fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 2 ,1 ] *
fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 4 ,1 ] * fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 1 ,1 ] * Ic ) ) -
fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 3 ,1 ]
} uniroot ( Ic , c ( 0 ,50 ) ) $ root Code # 光饱和点 Isat <- function ( Isat ) { ( 1 / ( 2 * fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 4 ,1 ] ) ) * ( fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 2 ,1 ] *
Isat + fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 1 ,1 ] - sqrt (
( fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 2 ,1 ] * Isat + fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 1 ,1 ] ) ^ 2 -
4 * fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 2 ,1 ] * fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 4 ,1 ] *
fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 1 ,1 ] * Isat ) ) -
fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 3 ,1 ] - ( 0.9 * fitlrc_nrec $ coef [ 1 ,1 ] ) }
uniroot ( Isat , c ( 0 ,2000 ) ) $ root Code # 使用ggplot2进行作图并拟合曲线 library ( ggplot2 ) light <- data.frame ( lrc_Q = lrc $ PARi , lrc_A = lrc $ Photo ) nonrec_form <- y ~ ( 1 / ( 2 * theta ) ) * ( alpha * x + Am - sqrt ( ( alpha * x + Am ) ^ 2 -
4 * alpha * theta * Am * x ) ) - Rd
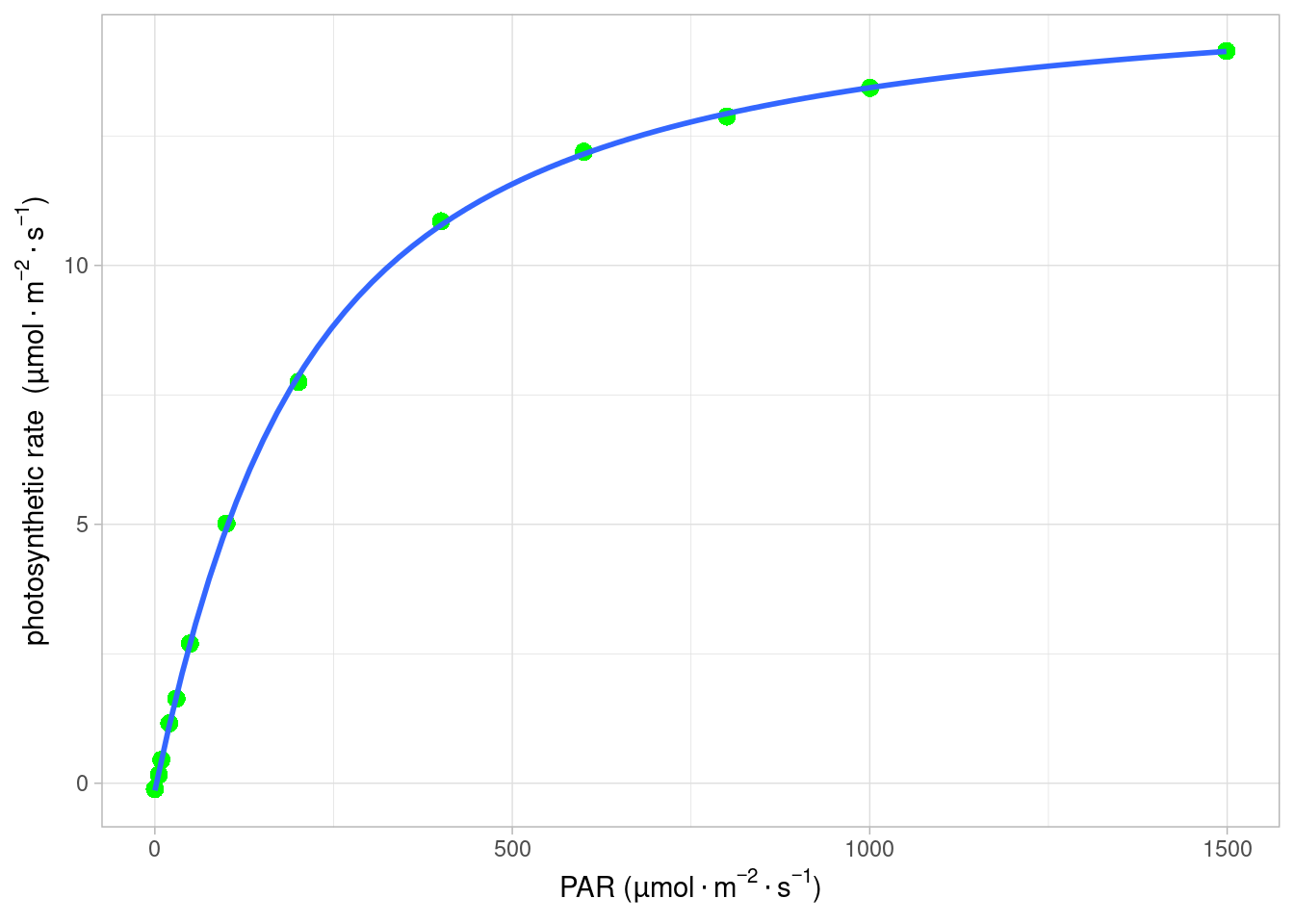
ggplot ( light , aes ( x = lrc_Q , y = lrc_A ) ) + geom_point ( shape = 16 , size = 3 , color = "green" ) +
geom_smooth ( method= "nls" , formula = nonrec_form , se = FALSE ,
method.args = list ( start = c ( Am= ( max ( lrc_A ) - min ( lrc_A ) ) ,
alpha= 0.05 , Rd= - min ( lrc_A ) , theta= 1 ) ,
aes ( color= 'blue' , size = 1.2 ) ) ) +
labs ( y= expression ( paste ( "photosynthetic rate " ,
"(" , mu , mol %.% m ^ - 2 %.% s ^ - 1 , ")" ) ) ,
x= expression ( paste ( "PAR " ,
"(" , mu , mol %.% m ^ - 2 %.% s ^ - 1 , ")" ) ) ) +
theme_light ( )
Table 9.1: 非直角双曲线模型结果
Am
15.8017296
0.1513064
104.435285
0.0000000
alpha
0.0658067
0.0020216
32.551422
0.0000000
Rd
0.1461717
0.0420800
3.473659
0.0070082
theta
0.3700908
0.0493403
7.500783
0.0000369
最终的数据拟结果如图 Figure 9.1 所示,拟合的参数及结果见表 Table 9.1 。单纯从作图来看,本例数据使用非直角双曲线与散点图重合程度更高。
利用函数来拟合
上面的方式是手动实现,也并不复杂,phtosynthesis 和 FitAQ 软件包提供了非直角双曲线模型 的相应的函数,可以让我们方便的进行处理。
使用 photosynthesis 处理
安装可以通过 CRAN:
我们看一下 LI-6400 数据的使用:
他的拟合结果的查看方式为:
Code
Formula: A_net ~ aq_response(k_sat, phi_J, Q_abs = data$Q_abs, theta_J) -
Rd
Parameters:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
k_sat 15.801730 0.151306 104.435 3.43e-15 ***
phi_J.Q_abs 0.065807 0.002022 32.551 1.20e-10 ***
theta_J 0.370091 0.049340 7.501 3.69e-05 ***
Rd.(Intercept) 0.146172 0.042080 3.474 0.00701 **
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 0.06845 on 9 degrees of freedom
Number of iterations to convergence: 6
Achieved convergence tolerance: 1.49e-08
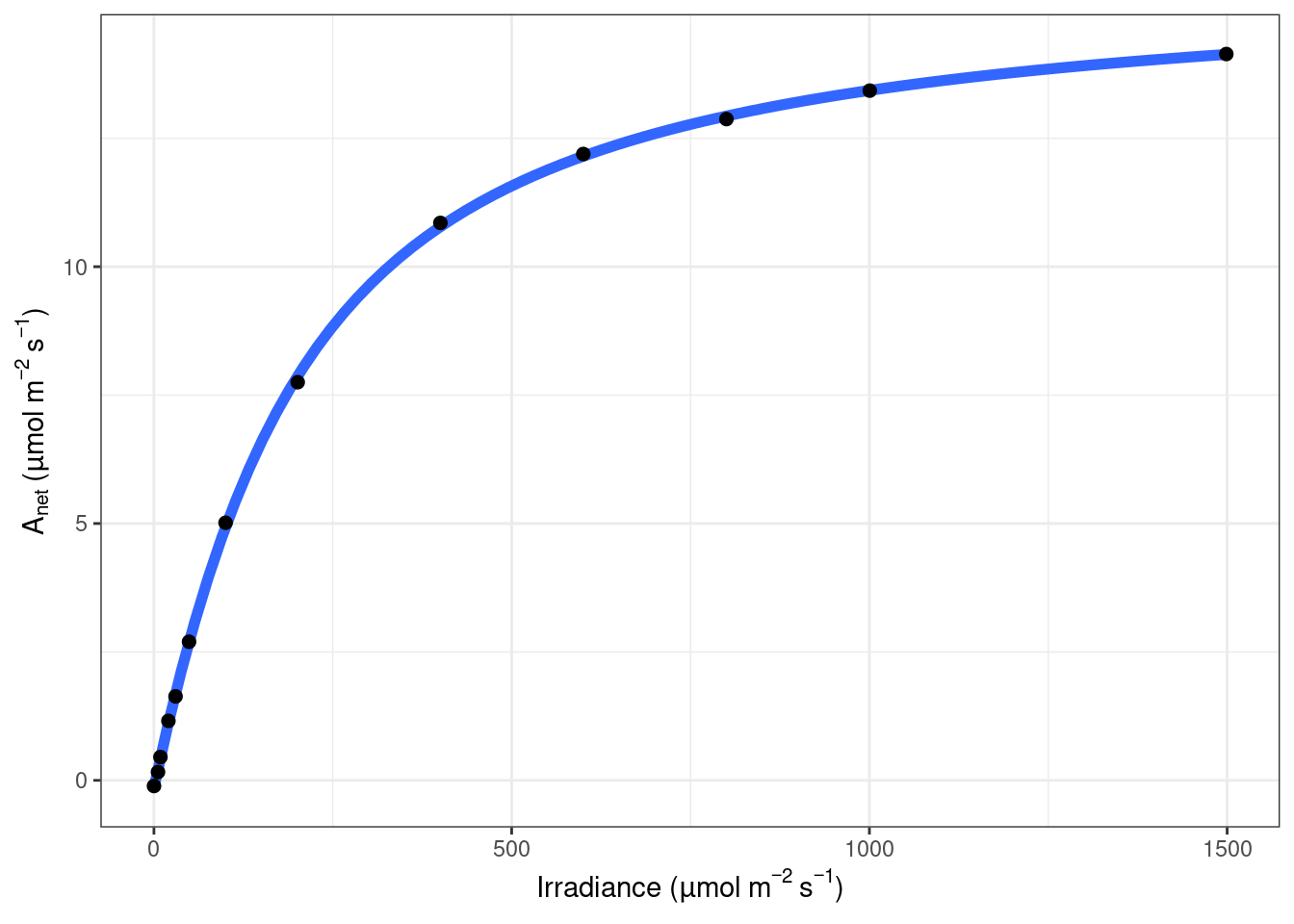
除此以外,它还提供了只看拟合结果的方式:
Code
A_sat phi_J theta_J Rd LCP resid_SSs
k_sat 15.80173 0.06580668 0.3700908 0.1461717 2.234292 0.04216531
他们的意义按顺序为:
饱和光下的净光合速率 (A_sat),
表观量子效率 (phi_J),
曲线的弯曲程度 (theta_J),
暗呼吸速率 (Rd),
光补偿点 (LCP),
残差的平方和 (resid_SS)。
也可以直接输出图形,只不过要想定制化,还要自己做:
如果是 LI-6800,稍微修改一下参数即可,这里不再进行一步一步的演示:
使用 FitAQ 处理
安装必须是从 github 安装,当然,如果你和我遇到一样登录 github 困难的话,我把他 fork 到 gitee 上去了:
使用也比较方便,默认这样操作就行了:
Code
Amax phi Rd theta
Amax 15.80173 0.06580667 0.1461717 0.3700909
如果觉得不满意,还可以手动调整初值,作者考虑的比较周到:
Code fit1 <- FitAQ ( data = lrc ,
A = Photo ,
Q = PARi ,
provide.model = TRUE ,
nlscontrol = c ( maxiter = 500 ) ,
start = list (
Amax = 15 ,
phi = 0.06 ,
Rd = 0.14 ,
theta = 0.3
) ,
lower = c ( 12 , 0 , 0 , 0 ) ,
upper = c ( 17 , 0.1 , 3 , 0.5 ) ,
trace = TRUE
)
0: 2.6244459: 15.0000 0.0600000 0.140000 0.300000
1: 0.021848654: 15.7837 0.0658725 0.146820 0.377608
2: 0.021082662: 15.8019 0.0658089 0.146186 0.370045
3: 0.021082654: 15.8017 0.0658067 0.146172 0.370090
4: 0.021082654: 15.8017 0.0658067 0.146172 0.370091
Code
Formula: A ~ ((phi * Q + Amax - sqrt((phi * Q + Amax)^2 - 4 * theta *
phi * Q * Amax)))/(2 * theta) - Rd
Parameters:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
Amax 15.801729 0.151306 104.435 3.43e-15 ***
phi 0.065807 0.002022 32.551 1.20e-10 ***
Rd 0.146172 0.042080 3.474 0.00701 **
theta 0.370091 0.049340 7.501 3.69e-05 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 0.06845 on 9 degrees of freedom
Algorithm "port", convergence message: relative convergence (4)
Code predict_range <- data.frame ( Q = seq ( from = 0 , to = 3000 , by = 20 ) ) addline <- within ( predict_range , A <-
predict ( fit1 , newdata = predict_range ) )
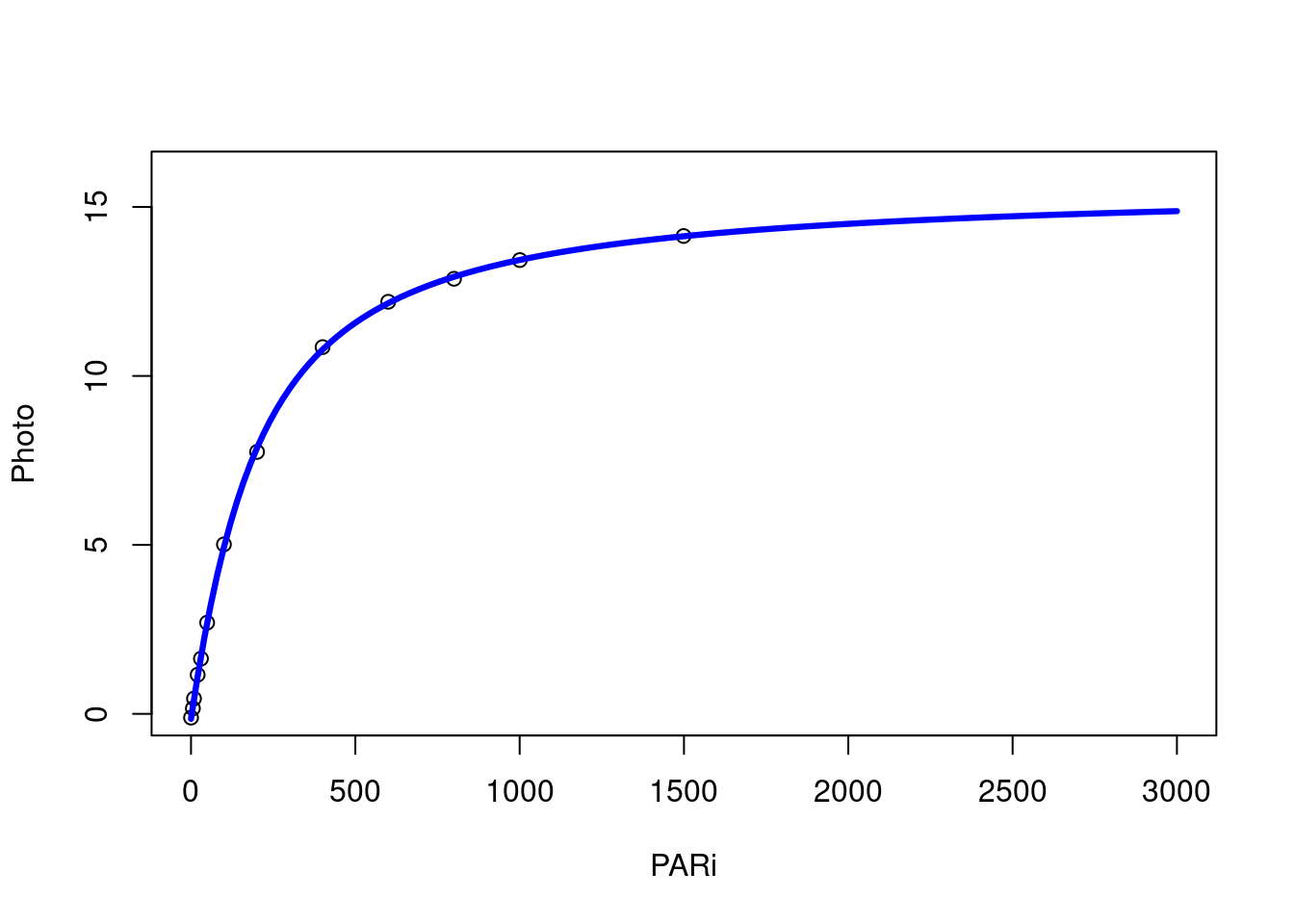
plot ( Photo ~ PARi ,
data = lrc ,
xlim = c ( 0 , 3000 ) ,
ylim = c ( 0 , 16 )
) lines ( A ~ Q , data = addline , col = "blue" , lwd = 3.2 )
这里需要说明,FitAQ 作者使用的 base R 的语法,而 photosynthesis 则喜欢 ggplot2,这两个谈不上优劣,只是相比而言,photosynthesis 把一些细节都做了,出结果比较省事,但是要做一些定制化图形的时候没有接口,而 FitAQ 则把细节美化留给用户自己来操作,但出基本结果的时候代码量会大一些。定制程度更高一些。
这里做拟合曲线图形的时候用了一个小技巧,与我 Figure 9.1 所采用的方式完全不同,我的作图实际上是强行把非线性拟合放到 ggplot2 内,而这里不需要拟合过程,只需要参数带入模型,得出数据点来,只要数据点足够密集,我们用线连接所有数据点后,看上去就是一条平滑的曲线,这种方式虽然是欺骗,但是并没有错误,数据点足够密集,我们根本看不出是点还是线来。
饱和点和补偿点的计算也提供了方便的函数:
Code
Code
Code FitSat ( fit1 , sat.fac = 0.95 , range = c ( 0 , 3200 ) )
饱和点也是使用了达到最大饱和光强多少比例时候的值,带入模型求的光强而得到,例如这里修改后使用了 0.95,看上去结果就不不正常了。
至于 LI-6800 的分析,也是一样,修改光合速率和光合有效辐射两个参数的名称即可:
Code aq6800 <- read.csv ( "data/lrc6800.csv" ) FitAQ ( data = aq6800 , A = A , Q = Qin )
Amax phi Rd theta
Amax 39.05857 0.063463 3.243814 0.7451511
为了减少篇幅,不在展开做过多的介绍,使用方式和上面演示的 LI-6400 一致。
Thornley, J H M. 1976. 《Mathematical models in plant physiology》 . London: Academic Press .